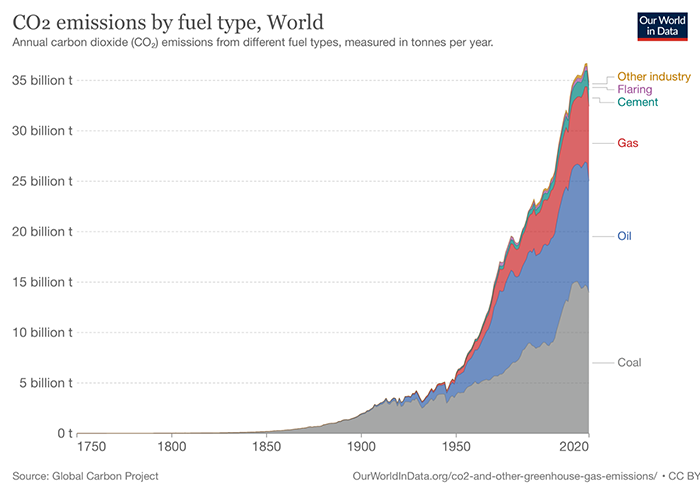
As early as the 18th century, the United Kingdom began to use coal in large quantities because of its industrialization. In the 19th century, Europe and the United States also joined. In the 20th century, more countries began to use coal, which greatly increased the carbon emissions of coal burning. In 1913, the carbon dioxide emissions were about 32.8 million tons. The United States accounted for nearly 40%. In the world at that time, coal was used as the main energy source in industry, power generation, and train power. With the development of oil and natural gas, other alternative energy sources have begun, and the proportion of renewable energy (wind, solar, etc.) has also increased in recent years. However, even with different energy sources, up to now, coal-fired carbon dioxide emissions still account for 40% of the total (grey area in the figure below), with an annual emission of 140 million tons.
COP26 reaches first world coal-burning agreement
Posted in Care About
Why does ‘coal’ need to be phased out?
About 40% of the world’s electricity is generated from coal. Coal-fired power plants have low cost and are more stable and safer than oil and natural gas. However, the sulfides and nitrides released by burning coal contribute to air pollution and generate a lot of energy. Greenhouse gases (methane and carbon dioxide), according to the US Energy Administration’s analysis of the country’s single power plant data,using coal, natural gas and oil to generate electricity, with natural gas providing the highest amount of electricity, followed by coal, and oil is the lowest, but if you compare the amount of carbon dioxide produced, coal-fired is the highest, with the same output of 1 kilowatt of electricity, coal-fired emissions are more than twice that of natural gas. This is why even coal is cheap, but if you add the cost of greenhouse gases, coal still be the energy raw material that needs to be phased out first.”
Is it difficult to reach a consensus on the coal agreement at the 2021 United Nations Climate Summit (COP26)?
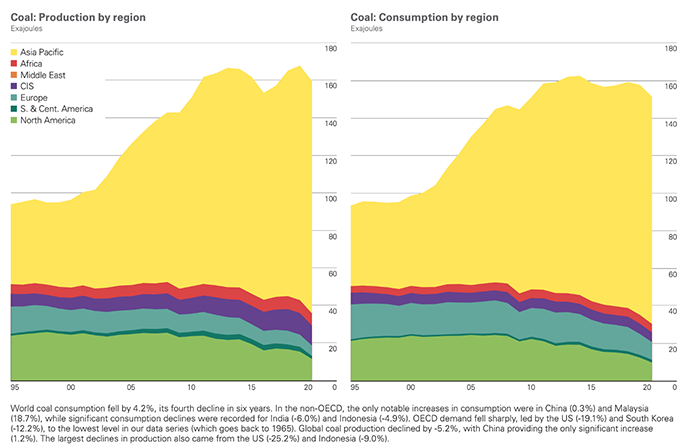
The price of coal-fired power generation is low. Most countries will give priority to coal-fired power generation due to cost considerations in the early stage of development. However, with the gradual maturity of different energy generation technologies and the improvement of environmental awareness, they are more willing to use other options (natural gas, or other renewable energy such as solar and wind energy) when building new power plants. Looking at coal use around the world from the graph below, Asia (yellow blocks) and North America (light green blocks) are currently the top two in terms of usage. In recent years, coal use in North America has begun to decline due to policy changes including Canada and the United States, among other reasons. Asia is still increasing.
至今,有些國家仍仰賴煤炭發電,煤炭發電量前幾名:中國、印度、美國、日本、南韓、南非,如下圖 。美國現在仍服役中的燃煤發電廠,大部分於1970、1980年代建造,皆達到使用年限,2022年,美國預計會將國內85%的燃煤發電廠關閉,包含位於俄亥俄州全美最大的燃煤發電廠,並會將太陽能發電提高至該國總供電量的一半。
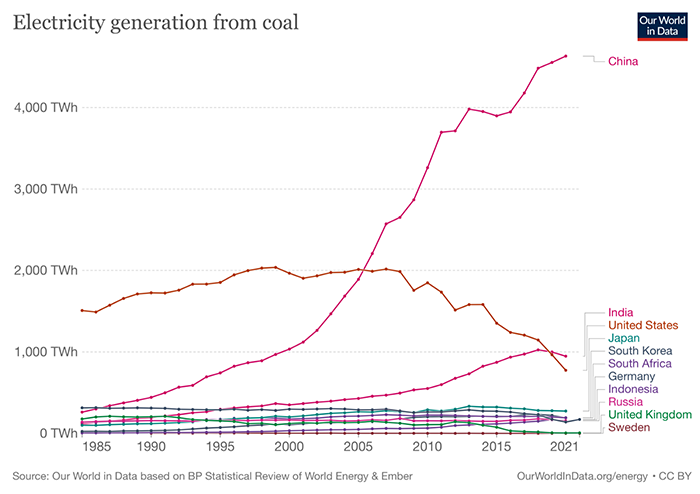
So far, some countries still rely on coal power generation. Coal-fired power generation tops the list: China, India, the United States, Japan, South Korea, and South Africa, as shown in the figure below. Most of the coal-fired power plants still in service in the United States were built in the 1970s and 1980s and have reached their end of life. By 2022, the United States is expected to close 85% of its domestic coal-fired power plants, including the largest one in Ohio. And will increase solar power to half of the country’s total electricity supply.
In Asia, coal accounts for more than half of the fuel for electricity supply in China and India (as shown in the chart below). Compared with Europe and the United States, coal-fired power plants are relatively young and have a long service life, making it more difficult to operate in these regions. A deal to phase out coal is difficult to agree on at COP26.
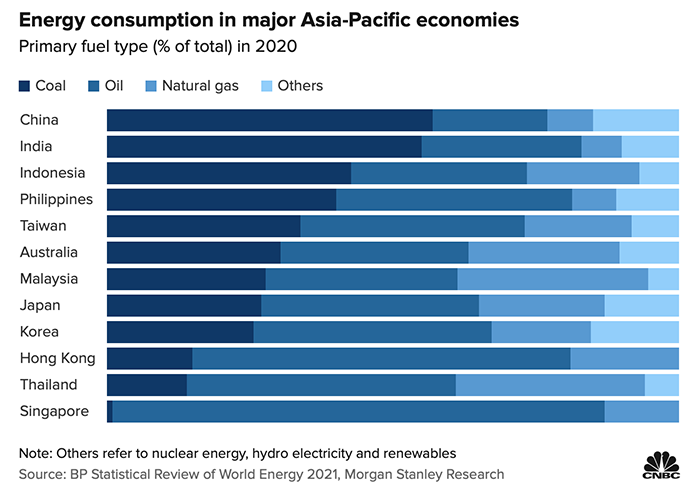
Elsewhere, coal use in Africa is lower than in Asia and North America, but more than 90 percent of the region’s electricity is powered by coal, making a common deal difficult.
Currently, there are 8,500 coal-fired power plants in operation around the world, and there are still plans to build more in developing countries. Nearly 40% of the world’s electricity generation produces irreversible greenhouse gases. Therefore, in climate action, countries using alternative energy sources to generate electricity and gradually reducing/phasing out the use of coal will certainly effectively reduce carbon dioxide emissions. COP26, for the first time, reached a written agreement between countries to explicitly reduce the use of coal, which also highlights the importance of the coal-fired agreement at the meeting.
Written By:陳韋廷
References:

