Why does ‘coal’ need to be phased out?
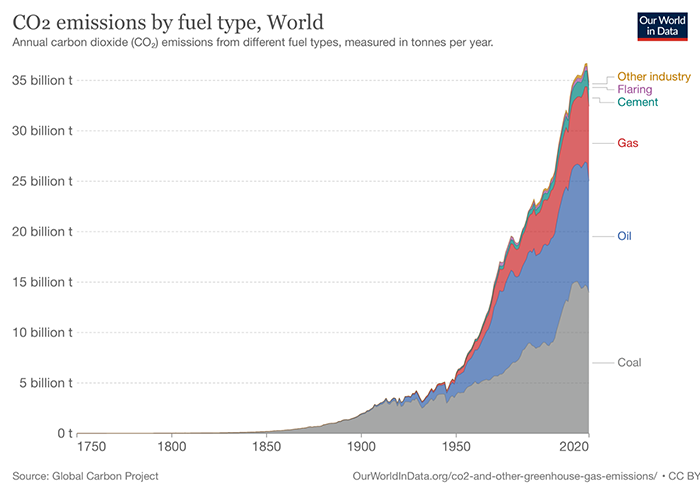
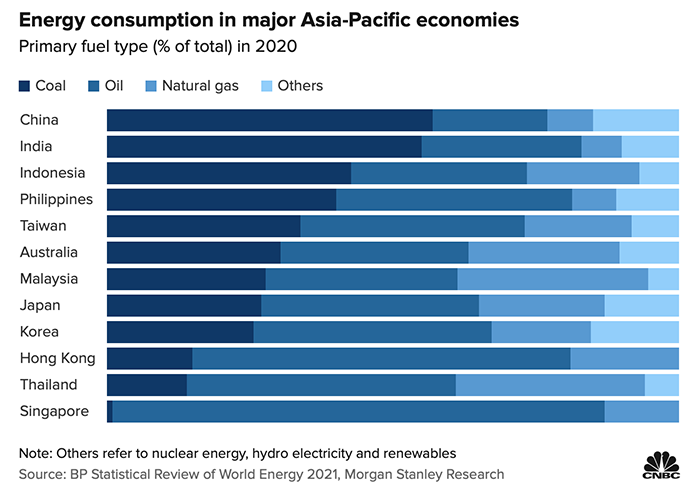
About 40% of the world’s electricity is generated from coal. Coal-fired power plants have low cost and are more stable and safer than oil and natural gas. However, the sulfides and nitrides released by burning coal contribute to air pollution and generate a lot of energy. Greenhouse gases (methane and carbon dioxide), according to the US Energy Administration’s analysis of the country’s single power plant data,using coal, natural gas and oil to generate electricity, with natural gas providing the highest amount of electricity, followed by coal, and oil is the lowest, but if you compare the amount of carbon dioxide produced, coal-fired is the highest, with the same output of 1 kilowatt of electricity, coal-fired emissions are more than twice that of natural gas. This is why even coal is cheap, but if you add the cost of greenhouse gases, coal still be the energy raw material that needs to be phased out first.”
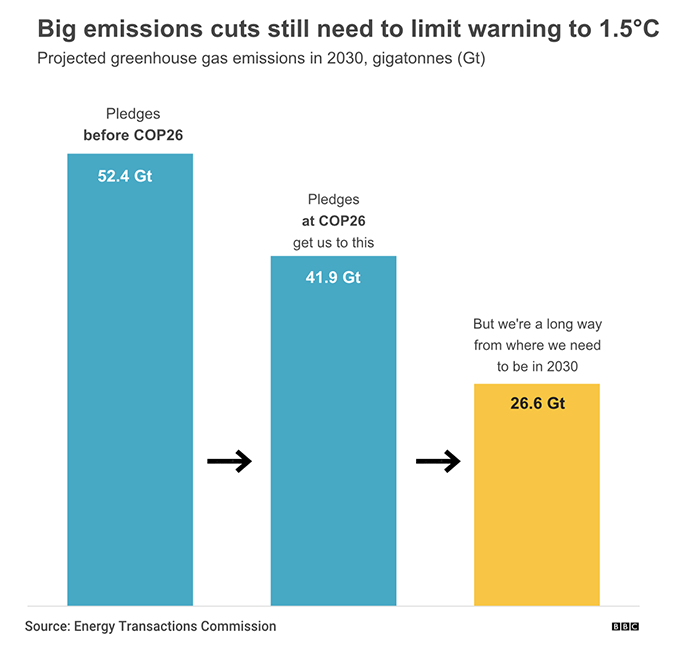
Is it difficult to reach a consensus on the coal agreement at the 2021 United Nations Climate Summit (COP26)?
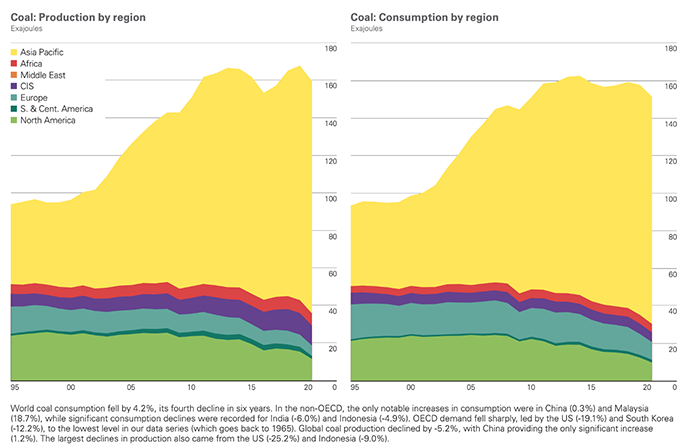
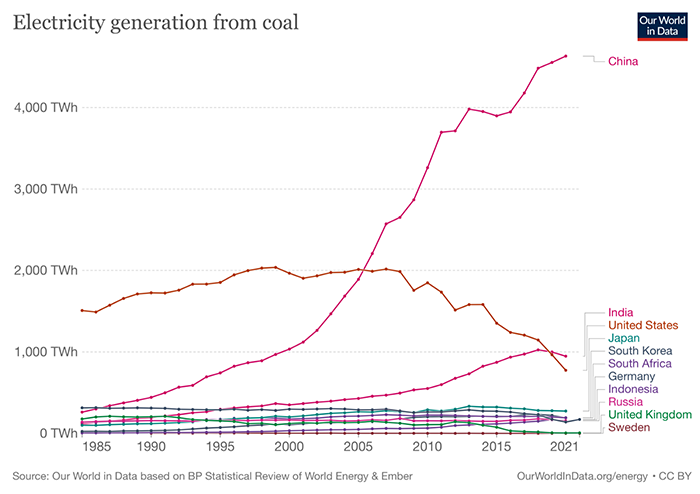
The price of coal-fired power generation is low. Most countries will give priority to coal-fired power generation due to cost considerations in the early stage of development. However, with the gradual maturity of different energy generation technologies and the improvement of environmental awareness, they are more willing to use other options (natural gas, or other renewable energy such as solar and wind energy) when building new power plants. Looking at coal use around the world from the graph below, Asia (yellow blocks) and North America (light green blocks) are currently the top two in terms of usage. In recent years, coal use in North America has begun to decline due to policy changes including Canada and the United States, among other reasons. Asia is still increasing.